A Diseconomy of Scale Represents Which of the Following Conditions:
A rise in average costs due to an increase in the scale of production. As firms get larger they grow in complexity.
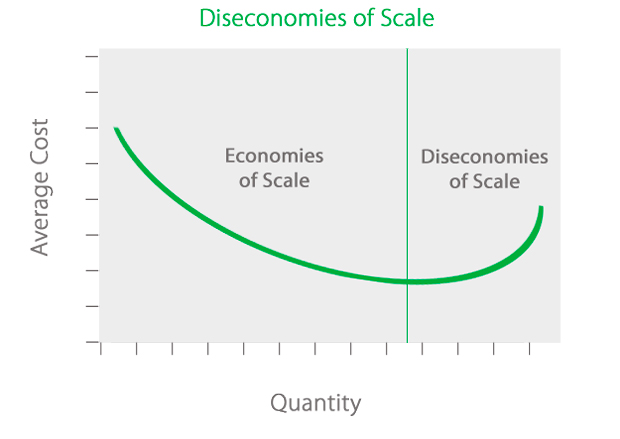
What Are Diseconomies Of Scale Definition Meaning Example
Diseconomies of scale occur when there is an increase in the long run average cost of production as output rises.

. Diseconomies pertain to a decrease in output associated with increased production due to diseconomies generated by growing large. Economies of scale also known as internal economies of scale describe a firms decrease in per-unit costs as production increases. - communication issues because lots of people working together in a business it can be difficult to ensure people are communicating.
When a business grows it can be challenging to maintain economies of scale. Meanwhile if the company passes the increased cost per unit on the selling price it will reduce its competitiveness. Diseconomies of Scale Diseconomies of scale occur when an additional production unit of output increases marginal costs which results in reduced profitability.
Diseconomies of scale occur when a business expands so much that the costs per unit increase. The two concepts explain the same phenomenon in just opposite ways. Diseconomies of scale have an impact on increasing operating costs.
Internal diseconomies of scale. Economies of scale often have limits such as passing the optimum design point where costs per additional unit begin to increase. Diseconomies of scale are often segregated into those arising from internal factors and those arising.
Internal diseconomies of scale include those arising from. A common limit for a low cost per unit weight commodities is saturating the regional. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function.
Assuming the selling price unchanged it leads to decreased profitability. Are diseconomies of scale that occur within a firm for a number of reasons. It is where prices of an item or product increase as output of the same item or product decreases.
Instead of the cost decreasing as more units are produced which happens with economies of scale they go up. Diseconomies of scale are the opposite. Common limits include exceeding the nearby raw material supply such as wood in the lumber pulp and paper industry.
Market share decreases as consumers switch to cheaper competing products. Diseconomies of scale defined is the inverse of economies of scale. Diseconomies of scale occur when an additional production unit of output increases marginal costs which results in reduced profitability.

Diseconomies Of Scale Main Causes And How To Avoid Them
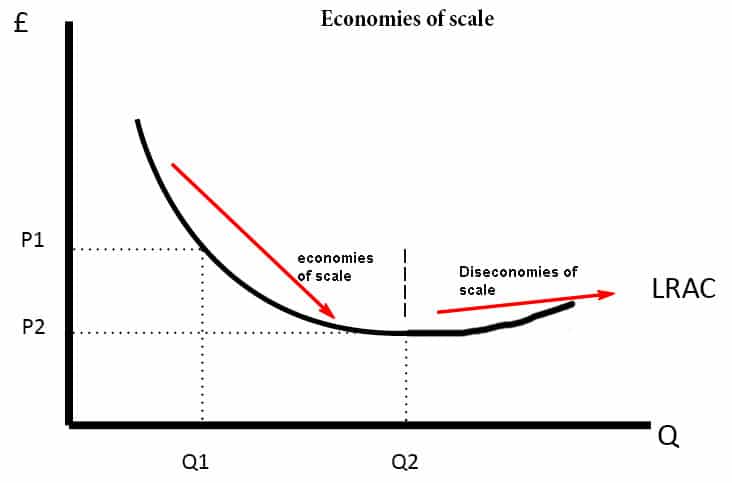
Decreasing Returns To Scale Economics Help

What Are Diseconomies Of Scale And Why They Matter Fourweekmba
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
Minimum Efficient Scale Mes Definition

Diseconomies Vs Economies Of Scale Graphs Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Diseconomies Vs Economies Of Scale Graphs Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Diseconomies Of Scale Examples Causes Of Diseconomies Of Scale

Diseconomies Of Scale Main Causes And How To Avoid Them
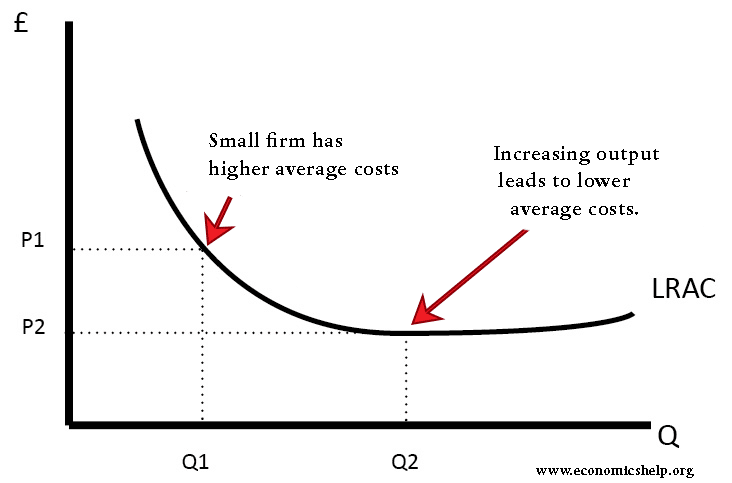
Economies Of Scale Examples Economics Help

Economies Of Scale Definition And 8 Examples Boycewire
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)
Diseconomies Of Scale Definition
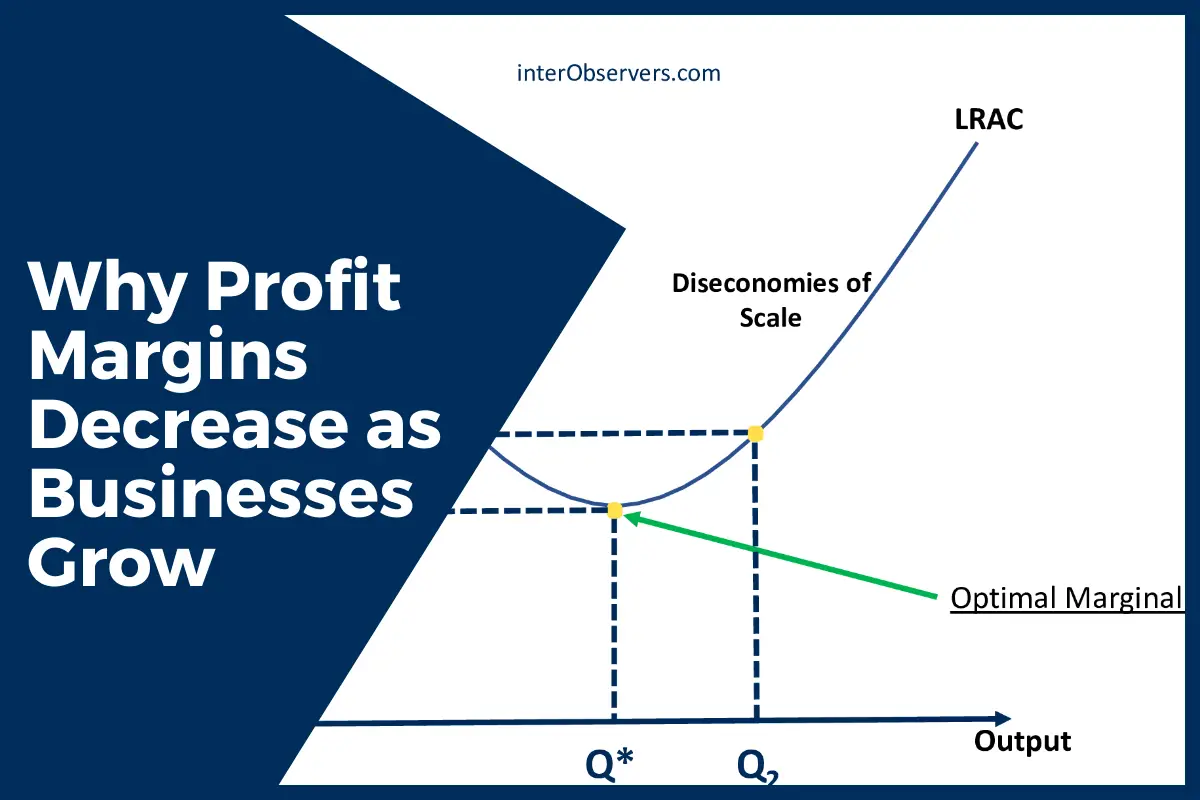
Diseconomies Of Scale Main Causes And How To Avoid Them
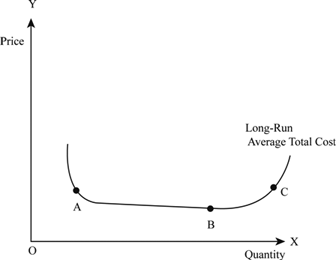
Definition Of Diseconomies Of Scale Chegg Com

Diseconomies Of Scale Types And Causes Penpoin

Decreasing Returns To Scale Economics Help
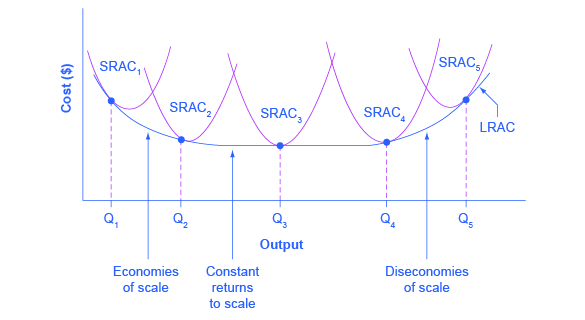
Economies Of Scale Microeconomics
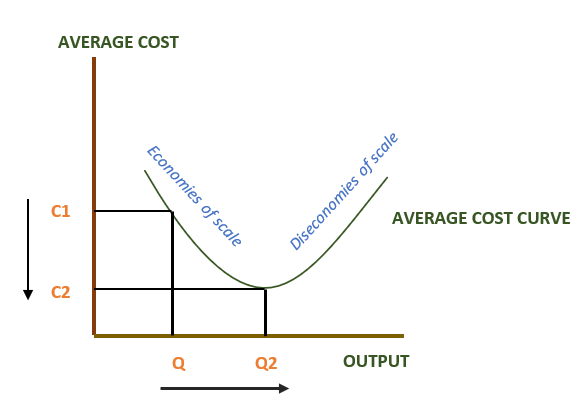
Diseconomies Of Scale Meaning Graphical Representation Example Efm
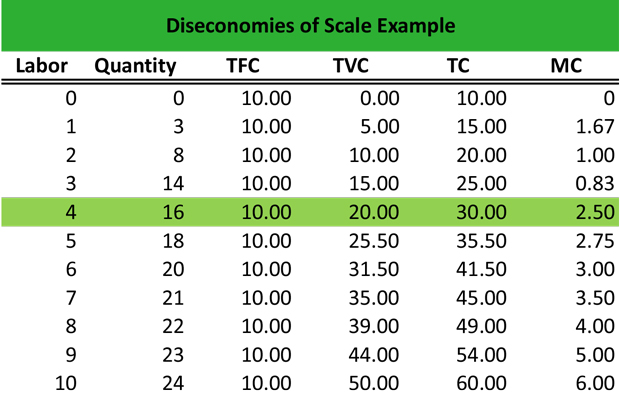
/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)
Comments
Post a Comment